Wednesday, December 19, 2007
Happy Vacation!
Sunday, December 16, 2007
While I'm on JUA
You should be working on your cancer pamphlets. E block: Mrs. Joslin will collect your pamphlets at the end of class on Tuesday. D block, I will collect yours in class.
Friday, December 14, 2007
Cancer Pamphlet
For information on specific types of cancer, click here.
Thursday, December 13, 2007
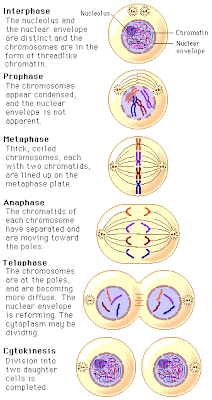
Mitosis and Cell Cycle Project
To see exemplary student samples from last year, click here.
Below are the guidelines for the project. This is due in class on Friday for E block and Saturday for F block.
REQUIREMENTS: Each Student MUST READ CHAPTER , focusing on ,
Draw, Label, and Define
A. INTERPHASE - THE TIME OF THE
B. MITOSIS (M PHASE) - A FOUR STAGE PROCESS WHICH THE NUCLEUS OF THE
C. CYTOKINESIS - THE CYTOPLASM
Monday, December 10, 2007
What would you do?
Sam (73) had a growth inside of his mouth for some time that he finally had checked out by his doctor. Following some tests, Dr. MacAvee, an oncologist, told Sam he had cancer of the gum (a squamous [skin] cell cancer). Unfortunately, the cancer had spread to Sam's lymph nodes in his neck and into his tongue and jaw. Dr. MacAvee told Sam they could do radical surgery to take out part of his tongue, the right side of his jawbone, and all of the lymph nodes in his neck, followed by chemotherapy and radiation treatment. Sam has refused. Sam's wife, Lois, seems reluctantly supportive of his decision. Sam's daughter, Michelle, has been lobbying Dr. MacAvee to convince her father to accept as aggressive a treatment as possible, so that Sam might have as much time as possible with his twin grand-daughters
What are the consequences of the course of treatment the doctor has suggested?
What is the likely prognosis (what will happen) for a metastatic skin cancer
Does Sam's decision to decline treatment make reasonable sense? Please discuss from the perspective of all people involved.
Homework: none :)
Friday, December 07, 2007
Cancer & You!
 E Block:
E Block:Objective: Complete a jigsaw activity for the cancer reading.
Students read a packet of information on cancer causes and treatments then shared their answers with a partner.
2. Choose a cancer that begins with the same letter as your first name (unless your name begins with an F or a J, then you can choose any cancer).
3. Write down:
a. the name of the cancer
b. a 3-5 sentence description of the cancer
c. how many new cases happen each year
d. how many deaths happen each year.
F block:
Objective: Examine the relationship between the cell cycle and cancer.
Students completed a review of the cell cycle worksheet, took notes from a powerpoint and had a discussion on cancer.
Homework: see above
Tuesday, December 04, 2007
Cell Cycle
Homework: Play the cell cycle game here and answer the questions on the worksheet you got in class.
Monday, December 03, 2007
Mitosis "Flip Books"
There should be one card/stage. The stages are: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis. On the front of each card should be a drawing of mitosis with the appropriate cell parts labeled (scroll down for pictures). On the back of the card should be the name of the stage and a description of what is happening in the cell and what number the stage is (1, 2, 3 or 4).
Homework: Complete the mitosis summary table worksheet. Extra credit: Mitosis coloring sheet.
Friday, November 30, 2007
Mitosis & Microscopes cont.
 E Block:
E Block: Objective: Students examined slides to see how a plant cell undergoes mitosis and compared plant cells to animal cells to observe the difference in cell division.
Today students looked at plant cells and after completing drawings, needed to find various stages of mitosis on their own on the slides as opposed to looking at slides that were already focused.
Homework: Read section 9.3 and complete the notetaking sheet. Answer the concept check questions for section 9.3, #1-3 on page 188.
Thursday, November 29, 2007
Mitosis & Microscope FOR THURSDAY E & FRIDAY F LONG BLOCKS
 Purpose: This activity follows the ABC educational theory (activity before concept). Students will draw the stages they see and answer questions about the slides. After answering questions independently, we will talk about the questions as a class.
Purpose: This activity follows the ABC educational theory (activity before concept). Students will draw the stages they see and answer questions about the slides. After answering questions independently, we will talk about the questions as a class.Homework: Read section 9.1 in the book and answer the concept check questions on page 181 # 1-3.
Wednesday, November 28, 2007
For the winter term only...
Why's this? Because E and F blocks each meet on either Tuesday or Wednesday for 55 minutes (therefore you'll be doing the same things).
Tuesday, November 27, 2007
New Unit: Cancer, Mitosis & the Cell Cycle
Objective: 1. Introduce the cell cycle, cancer and mitosis unit to the students. 2. Identify myths and truths about cancer.
Students competed a true/false quiz in teams to test their knowledge on cancer (don't worry it doesn't count as a quiz grade). We discussed each myth and explained if it was true or false.
Homework: None.
Friday, November 09, 2007
Food Lab: Bringing together the unit on Macromolecules.
Homework: Complete the questions in the lab handout, we will go over the questions and how you should write your lab report.
Thursday, November 08, 2007
Macromolecules Wrap Up
Homework: Bring in three different food samples. 1 that you think contains protein, one that you think contains MOSTLY starch and one that you think contains mostly fat.
Tomorrow we will be doing the Food Lab and you will get to see what your foods contain.
Tuesday, November 06, 2007
Peer Evaluation for Project
1. Out of 100% how much work did you do and how much work did your partner do? If you think you shared the work equally, you would write "I did 50% and my partner did 50%."
2. Were you pleased with the partner you had, or were you disappointed. Explain.
3. What did you learn about group work from this project.
4. On a scale of 1-10 (1 being the worst, 10 is the best). What score would you give your parter. You must write at least 3 sentences explaining your grade.
Monday, November 05, 2007
Personal Day
Friday, November 02, 2007
What are you going to say?
Homework: practice what you are going to say for the presentation.
Thursday, November 01, 2007
Projects cont.
Click here to link to the post with info on your topics and how to cite your sources.
Tuesday, October 30, 2007
Projects and returning the quizzes.
So the next logical question is: How can I raise my grade?
Answer: Do a really great job on your project. You will be working on it again in class today and on Thursday. I will also be available for extra help if you would like to practice your presentation on Thursday night in Moore House.
Homework: Work on your presentations.
Monday, October 29, 2007
Macromolecules Posters Links
Macromolecule Glossary
Macromolecules Overview
Lipids
Protein
Carbohydrates
Enzymes
Macromolecule Projects
What is a macromolecule? Well, break it up: Macro = big. Molecule = made up of atoms held together by chemical bonds.
Student Responsibilities
1. Read your assigned section of Chapter 5 in your textbook
2. With your partner, prepare a 15 minute presentation of your section
3. With your partner, prepare a poster that highlights the important concepts and vocabulary in your section. This should include text and pictures/diagrams. Make these artistic, neat, and informative; they will be on display in the classroom.
4. Make vocabulary cards of your section for the rest of the members of the class.
5. Create a handout for your classmates. You have been emailed a handout template.
6. Present your section on the Molecules of Life to the class.
You will be assessed by your teacher and your peers (in your group) on:
-your presentation
-your poster
-your vocabulary cards
-your ability to work in a group
-your contributions to the group effort
Homework: Read your assigned section and BRING NOTES TO CLASS on your section.
Friday, October 26, 2007
Quiz and Review of the Lab Reports
"What? This lab report is sooo long! Last year it took me like three minutes to write a lab report."
 Objective: 1. Go over the correct way to write a lab report and compare that to way you turned in. 2. Take a quiz on osmosis and diffusion.
Objective: 1. Go over the correct way to write a lab report and compare that to way you turned in. 2. Take a quiz on osmosis and diffusion.Handouts: sample lab report on brightly colored paper and the updated lab rubric on yellow paper.
Today we compared student's lab reports to the sample and we learned that writing lab reports will take more than 15 minutes. Never fear, next week you will have a project on macromolecules to work on and the following week you will have another chance to write a lab report.
Homework: none. Enjoy homecoming weekend. Please bring your books to class on Monday.
Thursday, October 25, 2007
Blue Planet
Homework: study for your quiz on osmosis, diffusion, cell membranes, membrane functions, concentration gradients and the scientific method. To link to a list of the vocabulary that you need to know for the quiz, click here.
Friday, October 19, 2007
Parents Weekend!
Homework: Study all of your vocab cards for a test on Friday when you return.
Thursday, October 18, 2007
Biology Board Games
Objective: Make biology board games to review and to play with your parents & grandparent tomorrow.
Homework: finish your board game and bring in dice.
Tuesday, October 16, 2007
Eggsperiment Lab Write Up
Today we reviewed each section of a scientific paper and the do's and don'ts for each section. Here's a quick summary:
DO:
* Write your section headings in bold and center them on the page (ex):
* List at least three sources of errors in the discussion section.
* Type the lab report
* Use the rubric (check your email)
DO NOT:
* Have a numerical list of the steps in the procedure or list of materials
* Use the first person "I, My" etc..
Have you "misplaced" the guide to writing scientific papers? Click here for the more elaborate version online.
Each person must turn in his/her own lab report, IN CLASS ON THURSDAY.
Monday, October 15, 2007
Eggsperiment Data
All classes should complete analysis questions 1-5.
Eggsperiment Results
Complete eggsperiment observations, data collection and analysis questions.
Today students looked at their eggs after they had been sitting in "secret" solutions over the weekend. Students will complete a data table using data from both E and F blocks.
Homework: Complete analysis questions 1-5 on the back of the lab sheet.
Friday, October 12, 2007
Eggsperiment!
What's the eggsperiment? Students used large chicken eggs which had the shell removed using vinegar, revealing a cell membrane. The eggs are then placed in various "secret" solutions of water, sucrose, table sugar and/or corn syrup. The eggs sit over the weekend and on Monday students will be able to see if osmosis and/or diffusion has occurred.
Homework: none.
 Long and Madison collect their egg.
Long and Madison collect their egg. Leo and Flash make primary observations of their egg.
Leo and Flash make primary observations of their egg. Kirsten and Emily find the initial mass of their egg.
Kirsten and Emily find the initial mass of their egg. Lindsey and Morgan work on their "secret" solution.
Lindsey and Morgan work on their "secret" solution. Max and Patt work on their "secret" solutions.
Max and Patt work on their "secret" solutions. E Blocks eggs. The control is the egg on the far left.
E Blocks eggs. The control is the egg on the far left. F Blocks eggs. The control is the egg on the far left.
F Blocks eggs. The control is the egg on the far left.Thursday, October 11, 2007
Membranes regulate the traffic of molecules
The plan:
complete reading quiz
finish membrane protein function notes
fill in guided notes on osmosis and diffusion
review
Homework:
Make Flash Cards for the 17 following words/concepts:
1. Phospholipid Bilayer
2. hydrophobic
3. hydrophilic
4. Components of a cell membrane (phospholipid bilayer, proteins, carbohydrates)
5. Four functions of membrane proteins (enzyme activity, cell-cell recognition, cell signaling, transport of materials)
6. Diffusion
7. Osmosis
8. Equilibrium
9. Passive Transport
10. Facilitated Diffusion
11. Hypertonic Solution
12. Isotonic Solution
13. Hypotonic Solution
14. Active Transport
15. Vesicle
16. Exocytosis
17. Endocytosis
Tuesday, October 09, 2007
Cell Membrane Structure

Today we had our first reading quiz of the year! Something that is likely to happen more often. Students needed to answer five questions about the reading and could use any notes they had taken. What did we learn from this experience?
"I guess I should have taken notes."
"I should have written down the homework."
Tonight's homework: If you haven't read section 6.3 read it and be ready for a reading quiz.
Extra Credit: Find the answers to "What happens if you get the wrong type of blood? How long can you live with the wrong type of blood?"
Monday, October 08, 2007
Lab Report Rubric
| Component | Criteria | Max. Points | Points Earned |
| Title | Includes the environmental factors that were manipulated, the parameter that was measured and the specific organism that was studied. | 5 | |
| Introduction | Includes the observation and question that led to the hypothesis, any relevant background information and the hypothesis. | 5 | |
| Materials and Methods | Describes (not lists) how the experiment was conducted. The equipment used in the experiment is NOT listed, instead is part of the narrative. If well-known methods were used without changes, simply name the methods (e.g., standard microscopic techniques). | 5 | |
| Results | Here the researcher presents summarized data for inspection using narrative text and, where appropriate, tables and figures to display summarized data. Only the results are presented. No interpretation of the data or conclusions about what the data might mean are given in this section. | 5 | |
| Formatting of tables or graphs | All tables or graphs have titles and a description explaining what is presented. | 5 | |
| Discussion | Here, the researcher interprets the data in terms of any patterns that were observed. The author should include any explanations of how the results differed from those hypothesized. Include at least 3 sources of error. | 5 | |
| Conclusion | This section simply states what the researcher thinks the data mean, and, as such, should relate directly back to the problem/question stated in the introduction. | 5 | |
| Acknowledgements | In this section you should give credit to people who have helped you with the research or with writing the paper. If your work has been supported by a grant, you would also give credit for that in this section. | 5 | |
| Literature Cited | This section lists, in alphabetical order by author, all published information that was referred to anywhere in the text of the paper. It provides the readers with the information needed should they want to refer to the original literature on the general problem. | 5 | |
| Spelling & Grammar | Report is free from spelling and grammatical errors. | 5 | |
| Total Points | | 50 | |
Quiz on Cell Parts
You also had a quiz on the parts of the cell, scientific method and microscope skills.
Homework: re-read section 6.2 and read section 6.3
Saturday, October 06, 2007
Plant Cell Wet Lab
Thursday, October 04, 2007
Chapter 6 vocabulary part 1
19 words
Section 6.1
Cell Theory
Organelle
Prokaryotic Cell
Eukaryotic Cell
Section 6.1 & Class notes
Plasma Membrane
Nucleus
Cytoplasm
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Mitochondria
Ribosome
Golgi body
Class Notes / Mini-lab Vocabulary
Flagellum
Pilus
Lipid
Protein
Amino Acid
Organelle
Cytoskeleton
Cell Parts Continued
Homework: Click here to use the interactive cells alive animation to answer the questions on the worksheet.

E block also did a mini lab to look at their own cheek cells using microscopes and methlyene blue.
Tuesday, October 02, 2007
Cells!
1. Explain the three parts of cell theory
2. Differentiate between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
3. Begin to identify organelles (cell parts) and their functions
Using a hand out on cell parts, students worked to create analogies between cell parts and their functions.
Homework: Read section 6.1 and answer the concept check questions on page 114. Read section 6.2 and answer the questions on page 117.
If you did not make the flash cards for last week, you still need to do that!
Thursday, September 27, 2007
Chapters 1 & 2 vocabulary
Section 1.2
1. species
2. domain
3. eukarya (domain)
4. unicellular organism
5. multicellular organism
Section 1.3
6. biological system
7. producers
8. consumers
9. homeostasis
Section 2.1
10. observation
11. data
12. inference
13. hypothesis
14. variable
15. controlled experiment
In your notes:
16. independent variable
17. dependent variable
18. qualitative observations/data
19. quantitative observations/data
20-25. Make one flash card for each of the following conversions:
1 Liter = 1000 milliliters
1 meter = 100 centimeters
1 meter = 1000 millimeters
1 millimeter = 10 centimeters
1 gram = 1000 milligrams
Metrics and Rip-o-Meters
 Objective: Review metric conversions & design and carry out an experiment.
Objective: Review metric conversions & design and carry out an experiment.How do you test the strength of a leaf?
Do dead leaves always rip more easily than living leaves?
Does how you try to rip the leaf matter?
How many leaves should you test?
 Today E block answered the Rip-o-Meter prelab questions and was able to conduct their experiments and collect leaves. F Block only had a chance to answer the prelab questions. Tomorrow E block will collect leaves and conduct their experiments.
Today E block answered the Rip-o-Meter prelab questions and was able to conduct their experiments and collect leaves. F Block only had a chance to answer the prelab questions. Tomorrow E block will collect leaves and conduct their experiments.Homework: none. enjoy the night off :)
Tuesday, September 25, 2007
Mix and Match Mass
1. Review basic metric measurements
2. Practice using a triple beam balance.
Today students completed the "Mix and Match Mass" Activity. The purpose this activity is to practice using a triple beam balance and making predictions about the mass of various objects.
Homework: Complete the units and measurements homework.
Monday, September 24, 2007
Experimental Design & Controls and Variables
The Plan:
1. Write in objective (3 minutes)
2. Review Homework (10 minutes)
3. Parts of an experimental design (15 minutes)
4. Practice identifying variables in the design (12 minutes)
5. Explain homework (5 minutes)
Homework: Complete the Simpson's controls and variables problem set.
Friday, September 21, 2007
What makes your Rice Krispies pop?
Any liquid with any viscosity will create the "snap, crackle, pop"
Jello or jam might be too heavy to hear the sound
Size effects how they pop
Shape effects how they pop
How stale they are
If there's a sugar coating, when the liquid dissolves it, the bubbles pop
Will a single Rice Krispie make a sound?
Different kinds of liquids will make different sounds (what happens if you use pond water)?
Apple Cider Vinegar
Skim Milk
Sugar
Water
Water and Vinegar
Milk and Water
Milk, Water and Vinegar
Turns out the reason why Rice Krispies pop is... watch the video and find out!
Homework: E block: read section 2.3 and answer questions 7-14
F block: write a hypothesis using "if...then..." and design a detailed experiment
Thursday, September 20, 2007
Science News
2. To learn about at least three scientific research findings.
Did you know...
...that a gene can actually limit the effectiveness of medicines that help people quit smoking?
...that bacteria can successfully treat cancer?
...crops can be genetically engineered to grow in poisonous soil?
Working in small groups. students shared their articles and had a discussion. After the small group work, we talked as a class about what people learned.
Homework: Read AND take notes on sections 2.1 and 2.2.
Tuesday, September 18, 2007
Chapter 1 Quiz
 Today students took an open notes quiz on Chapter 1. What's the deal with open notes quizzes? Well, your notes are only helpful if you can use them.
Today students took an open notes quiz on Chapter 1. What's the deal with open notes quizzes? Well, your notes are only helpful if you can use them.Homework: One of the major themes in Biology is "Biology and Society." For Thursday Sept. 20th (the next time class meets) bring in an article about current scientific research. Read the article, answer the questions on the handout and be prepared to share your article with the class.
If nobody else in the class has the same article as you, you will get extra credit.
Not sure where to look for articles or what qualifies are "good science research?"
Below is a list of websites that will have articles for you to choose from.
Research and News on the Earth and Climate
Research and News on Health and Medicine
Research and News on Plants and Animals
Research and News on Fossils and Ruins
Still not sure? Click here for a list of topics. Click on any of the words in blue to be taken to a page of articles on that topic alone!
Monday, September 17, 2007
5 Themes (cont.)
Homework: Study for the open notes quiz tomorrow on the following material:
sections 1.2 and 1.3, as well as microscope skills. Just because it is open notes, doesn't mean you shouldn't at least look over your notes ahead of time.
Friday, September 14, 2007
5 Themes in Biology
What we did:
E block completed a jig-saw activity and working with a partner, gave a mini-presentation on one of the following themes: form and function, energy and life, reproduction, cellular basis of life, interaction with the environment or biological systems.
F Long Block: After a 20 minute discussion on the five themes listed above, we set off on a walk towards the lower pond to see how many of the themes we could see in action. Armed with clipboards and magnifying glasses, we observed how an oyster mushroom on a tree is an example of an interaction with the environment and how a monarch butterfly has other species that imitate it for protection (an example of adaptation).
Homework: Read section 1.3 and complete the short answer essay questions on page 20. You must write 3-4 sentences for each questions and use complete sentences.
Heads Up: You have a quiz on Tuesday on sections 1.2, 1.3 and use of a microscope.
Thursday, September 13, 2007
Lab 1: Exploring Kingdoms with Microscopes
By the end of today you should be able to...
1. Successfully focus a slide using low (scanning) power, medium power and high power.
2. Differentiate between single celled organisms and multicelled organisms.
3. Make observations using a microscope and draw these observations.
4. Classify organisms based on relative size.
Homework: Complete parts 1 AND 2 of the analysis questions.
Tuesday, September 11, 2007
Lab Contract
Lab Safety Contract
PREPARE FOR LABORATORY WORK· Study laboratory procedures prior to class.· Never perform unauthorized experiments.· Keep your lab bench organized and free of apparel, books, and other clutter.· Know how to use the safety shower, eye wash, fire blanket and first aid kit.
DRESS FOR LABORATORY WORK· Tie back long hair.· Do not wear loose sleeves as they tend to get in the way.· Wear shoes with tops.· Wear lab coats during all laboratory sessions.· Wear safety goggles during all laboratory sessions.· Wear gloves when using chemicals that irritate or can be absorbed through skin.
AVOID CONTACT WITH CHEMICALS· Never taste or "sniff" chemicals.· Never draw materials in a pipette with your mouth.· When heating substances in a test tube, point the mouth away from people.· Never carry dangerous chemicals or hot equipment near other people.
AVOID HAZARDS· Keep combustibles away from open flames.· Use caution when handling hot glassware. · When diluting acid, always add acid slowly to water. Never add water to acid.· Use glycerin and twist slowly at the base when inserting glass tubing through stoppers.· Turn off burners when not in use.· Do not bend or cut glass unless appropriately instructed by teacher.· Keep caps on reagent bottles. Never switch caps.
CLEAN UP· Consult teacher for proper disposal of chemicals.· Wash hands thoroughly following experiments.· Leave laboratory bench clean and neat.
IN CASE OF ACCIDENT· Report all accidents and spills immediately.· Place broken glass in designated containers.· Wash all acids and bases from your skin immediately with plenty of running water.· If chemicals get in your eyes, wash them for at least 15 minutes with an eyewash.
By signing my name (first name, last initial only) I acknowledge that I have read the information above and agree to: (a) Follow the teachers instructions, (b) protect my eyes, face, hands and body during laboratory, (c) conduct myself in a responsible manner at all times in the laboratory, and (d) abide by all of the safety regulations specified above. If I am in violation of this contract I will accept responsibility for my actions.
Organization in Biology
Today students presented their syllabi posters and we explored biological classification in sections 1.1 and 1.2.
Homework: Sign the lab contract (in the post above) and complete the pre-lab reading and questions. No prelab = no lab = a zero.
Monday, September 10, 2007
F Block : Biology Is..
Post a comment and list at least 5 things you think you will learn about this year.
This must be completed before 8am.
How to post a comment:
1. Click on the word "comments" in the light blue box right below this post.
2. If a Security box pops up, just click "yes."
3. Type your comment in the box titled "Leave Your Comment."
4. Sign your comment with your first name and last initial only.
5. Choose the identity "anonymous."
6. Click the orange "publish your comment" box.
REMEMBER: Your syllabi poster is due in class tomorrow and you MUST bring your notebook to class.
E Block: Biology Is..
Post a comment and list at least 5 things you think you will learn about this year.
This must be completed before 8am.
How to post a comment:
1. Click on the word "comments" in the light blue box right below this post.
2. If a Security box pops up, just click "yes."
3. Type your comment in the box titled "Leave Your Comment."
4. Sign your comment with your first name and last initial only.
5. Choose the identity "anonymous."
6. Click the orange "publish your comment" box.
REMEMBER: Your syllabi poster is due in class tomorrow and you MUST bring your notebook to class.
Wednesday, May 02, 2007
Predessesors to current views on evolution
Objective: Students will take notes on Charles Darwin, Alfred Russsel Wallace, Jean Baptiste Lamark, Georges Cuvier, James Hutton, Charles Lyell and Thomas Malthus.
Homework: We now know that there are four major modes of evolution: mutation, migration, genetic drift and natural selection. Find one example for each of the four modes (one example for mutation, one for migration..)
Tuesday, May 01, 2007
How long ago did.....?
Homework: Answer the four questions on the handout. Please use a seperate sheet of paper.
Tuesday, March 27, 2007
Welcome Back
www.globalproblemslocalsolutions.blogspot.com
So head on over and see what all the fuss is about.
Friday, March 02, 2007
Homework over break
Have a great break!
Monday, February 26, 2007
Review Monday & Tuesday
1. Describe the difference between cytokinesis in animal cells and plant cells?
2. List two way that meiosis differs from mitosis.
3. How is cancer related to the cell cycle?
4. Describe the structure of a chromosome.
5. What is independent assortment, and how does it affect the genetic makeup of offspring cells?
6. Describe how you could determine if a dividing cell is an animal cell or a plant cell.
What structures would you look for?
7. Why is crossing over important?
8. Describe the relationship between the cell cycle and mitosis.
9. Describe the role that the spindle fibers play in mitosis.
10. Explain why Crossing-over is an important source of genetic variation.
11. What types of cells does mitosis occur in?
12. Explain the difference between a diploid cell and a haploid cell?
13. Explain the difference between cytokinesis in eukaryotic plant and animal cells?
14. What is Interphase? What makes up and occurs during each part of Interphase?
15. Explain the Difference (Contrast) between Sex Chromosomes and Autosomes?
16. What are homologous chromosomes?
17. What is the cell cycle?
Classical Genetics
1. Describe Mendel's two laws of heredity.
2. What happens during meiosis that would allow genes located on the same chromosome to separate independently of one another?
3. Give an example of a sex-linked disorder.
4. How can two individuals who are phenotypically “normal” for a disorder produce a child who is affected.
5. Distinguish between codominance and incomplete dominance. Give an example of each type of inheritance.
6. Define the terms, dominant and recessive.
7. Relate the events of meiosis to the law of segregation.
8. Give an example of a monohybrid cross.
9. Explain how you would use a Punnett square to predict the probable outcome of a monohybrid cross. Draw a Punnett square to demonstrate your monohybrid cross.
10. Explain the terms genotype and phenotype.
11. Explain the terms homozygous and heterozygous.
12. Draw a pedigree for a couple who are phenotypically normal for albinsim who produce 6 children, 3 boys and 3 girls. One girl and two boys are albino.
13. Give an example of a non-disjunction disorder and explain how it occurs.
14. List and explain four types of chromosomal mutations (non non-disjunction).
DNA replication, Transcription and Translation
1. When does DNA replication occur?
2. List at least three enzymes involved in DNA replication and explain their function.
3. Where does DNA replication occur?
4. Draw DNA replication from start to finish.
5. Explain the need for a leading strand and a lagging strand.
6. Explain what would happen if there were a malfunction in the cell and ligase were never produced.
7. Describe the structure and function of DNA
8. Name three scientists associated with early DNA research. Briefly describe their contributions.
9. List three ways that DNA differs from RNA
10. Where does transcription occur?
11. Why does transcription occur?
12. Where does translation occur?
13. When does translation occur?
14. What is a codon? How many codons can be produced? How many amino acids are there?
15. Describe the cell part that is most involved with translation. What does it do?
16. If there were a mutation (such as in insertion or deletion) in the DNA sequence what affect would that have during translation. Give a real-life example of this.
17. A mutation at which base pair (first, second or third) in a codon would have the LEAST affect on the amino acid produced? Explain your answer.
Friday, February 23, 2007
Bioethics & You (Friday & Saturday Classes)
Case Studies were taken from the High School Bioethics Project and included the following briefs:
1. Patenting Life: Chakrabarty (bacteria engineered to "eat" crude oil)
2. Patenting Life: Of (spliced) Mice and Men (the Harvard Oncomouse)
3. Food & Drinks: GM Wine (GM grapes that grow in Florida)
4. Food & Drinks: Starlink Corn (Corn made for animal consumption and ended up in the human food supply)
5. Food & Drinks: GM Coffee (Coffee that can be ripened by the addition of a chemical)
6. The Forest for the Trees: GM Trees for paper production
There are only 2 more classes before the final exam!
General Bio homework: Complete pages: 77,79,81,83,85 and 87 in the review packet. This will take you about an hour and is due in class on Monday
Wednesday, February 21, 2007
Review Sheet for Final Exam
Below is a check list for all of the things that will be covered on your final exam. This is your review sheet.
1. Describe the cell cycle and the process of mitosis.
2. Explain the role of mitosis in the formation of new cells
3. Describe how the process of meiosis results in the formation of haploid cells.
4. Explain the importance of meiosis in sexual reproduction
5. Explain how gametes form diploid zygotes in the process of fertilization.
6. Compare and contrast a virus and an animal or plant cell in terms of genetic material and reproduction. (we covered this on the History of DNA movies handout – Bacteriaphages & Radioactive tracers)*
7. Describe the basic structure (double helix, sugar/phosphate backbone, linked by complementary nucleotide pairs) of DNA
8. Describe DNA’s function in genetic inheritance.
9. Describe the basic process of DNA replication (*honors classes need to know all the enzymes involved, direction of replication, leading and lagging strands etc.)
10. Explain how DNA replication relates to the transmission and conservation of the genetic code.
11. Explain the basic processes of transcription and translation, and how they result in the expression of genes (creation of amino acids, which create proteins which affect genes)
12. Distinguish among the end products of replication, transcription, and translation.
13. Explain how mutations in the DNA sequence of a gene may or may not result in phenotypic change in an organism.
14. Explain how mutations in gametes may result in phenotypic changes in offspring.
15. Distinguish among observed inheritance patterns caused by several types of genetic traits
a. dominant
b. recessive
c. codominant
d. sex-linked
e. incomplete dominance
16. Describe how Mendel’s laws of segregation and independent assortment can be observed through patterns of inheritance
17. Use a Punnett Square to determine the probabilities for genotype and phenotype combinations in monohybrid crosses.
18. Explain how cancer is related to the cell cycle.
A test & Review
Honors bio had a review session for their test tomorrow.
Monday, February 19, 2007
Notebook Quiz and Science News
Thursday, February 15, 2007
DNA replication, transcription and translation project
Chloe, Carson & David's Movie
Olivia & Carol's Blog
Bruce, Mike and Paul's MySpace
Andrea's Poster
Kali's Poster and Mike's Book (as well as some dragons)
Nick's Foam-Core Cut Outs
Jess & Sayde's Candy Poster
Chloe, Carson & David's movie
Olivia & Carol Blog
Click here to check it out.
MySpace & Science?? Whhhhatt? Bruce, Mike and Paul take it to a new level
Kali's Poster & Mike's Book

Jess & Sayde's Project

Wednesday, February 14, 2007
Independent Work & A Snow Day!
Tuesday, February 13, 2007
Honors Test Update
Your test is worth 50 points and will be combined with your project grade.
Here's what your test includes:
1 misc. question
2 questions on the history of the discovery of DNA
7 questions on transcription & translation
15 questions on the structure and replication of DNA
DNA replication, transcription, translation
Objective: Students will use the following activities online to learn DNA replication along with transcription & translation. Students will complete guiding questions while working on the activities.
Homework: Work on project.
Honors Biology: Students are working on their projects in class.
Saturday, February 10, 2007
Links to Student Work
Biology Honors Due Dates
The test is on Monday February 18th and is worth 50 points. Here is the breakdown of the test:
21 multiple choice questions and 4 true/false.
Friday, February 09, 2007
No 54321 this week and no class monday
Transcription & Translation
 Honors classes only for 2/9 and 2/10
Honors classes only for 2/9 and 2/10Admit Slip: Explain this pick up line "I wish I were DNA Helicase, so I could unzip your jeans"
Objective: Review the DNA replication homework. Students will take notes on Transcription & Translation and be able to identify the major stages as well as if the process takes place inside or outside of the nucleus.
Homework: Start working on your project. The guidelines were emailed to you and are posted below.
PROJECTS MUST BE TURNED IN ON TIME. EACH DAY THE PROJECT IS LATE, YOU WILL LOSE 15 POINTS. AFTER THE THIRD DAY, THE PROJECT WILL NO LONGER BE ACCEPTED.
What is it? (4pts)
Where does it occur? (1pt)
How does it happen? (4pts)
2. Transcription (10 points):
What is it? (4pts)
Where does it occur? (1pt)
When does it happen? (1pt)
How does it happen? (4pts)
3. Translation (10 points):
What is it? (4pts)
Where does it occur? (1pt)
When does it happen? (1pt)
Project is creative, original and aesthetically pleasing.
5. Content & Grammar (10 points):
Project contains no scientific, spelling or grammatical errors.
PROJECTS MUST BE TURNED IN ON TIME. EACH DAY THE PROJECT IS LATE, YOU WILL LOSE 15 POINTS. AFTER THE THIRD DAY, THE PROJECT WILL NO LONGER BE ACCEPTED.
Thursday, February 08, 2007
Your DNA & Valentines Day
Nothing Says 'I Love You' Like Framed Genetic Code
Weekend Edition Sunday, February 4, 2007 · So you're feeling pressure to come up with a deeply personal Valentine's gift. How about original art, made from your DNA? Adrian Salamunivoc runs a Web site that allows you to order just such a present.
Wednesday, February 07, 2007
Tuesday, February 06, 2007
History of the Discovery of DNA
Objective: Students will use a graphic organizer to take notes on a serries of mini-video clips from www.unitedstreaming.com which explain the contributions of the following scientists:
Friedrich Meisher: 1870
Fredrick Griffith: 1928
Avery, MacLeod and McCarty: 1944
Watson & Crick 1953
Homework: Use the DNA replication animation (available by clicking here) to complete the notes organizer. If for whatever reason you don't have a Flash player on your computer, you can use your textbook to find the information.
Monday, February 05, 2007
Mental Inventory
NOTE: Since we had a review in class, you recieved the packet (and the answers to all the multiple choice questions) THERE ARE NO TEST CORRECTIONS.
Saturday, February 03, 2007
Answer Key & 54321 reminder
.......the 54321 is due Sunday night by 9:30pm. If you turn it in at 9:31 it's late. Do yourself a favor and finish in the afternoon.
.......the answers to the review sheet have been emailed to you.
Blood Feud
We read and discussed the article Blood Feud (available by clicking here)
Our discussion not only included material from the article but also touched on:
Colonization of Africa by European countries
the African Union
(who would have thought history and biology would ever actually come together...)
We also had a visit from Whitey...BE WARNED: IF YOU ARE TROLLING OUTSIDE OF MY CLASSROOM YOU WILL BE INVITED IN AND PARTICIPATE.
B block:
reviewed for the test on Monday.
Friday, February 02, 2007
Review Packet via Email
there is a review packet.
some of the questions on the exam may have even been taken from the packet....
an answer key will be available on monday night.
Thursday, February 01, 2007
Exceptions to Mendel's Laws (A block only)
Objective: Review questions from Dragon Genetics and complete sample problems for sex-linked traits.
Homework: Complete the test cross problem set.
Wednesday, January 31, 2007
Dragon Genetics (Wednesday Jan. 31 & Thursday Feb.1)

Thursday, January 25, 2007
Test 2
General Biology you have a test on Tuesday February 6th, 2007.
Both tests will include the following material (degree of difficulty for the questions will vary between honors and general).
Meiosis and how it compares to mitosis
What is the importance of meiosis?
Examples and consequences of nondisjunction
Chromosomal Mutation
Basic Genetics (Mendel's Laws, punnett squares, test crosses)
Using a pedigree to track autosomal and sex linked disorders
Tuesday, January 23, 2007
Intro to Genetics: Jan. 22-Jan. 25
Objective: Students will complete the Intro to Genetics packet over two class periods. Concepts covered include: gametes, zygotes, alleles, homozygous, heterozygous, dominant allele, recessive allele, monohybrid crosses using punnett square, probability, pedigrees, albinism, dwarfism, genotype, phenotype and SRY sex determination.
Homework: Complete questions 1-5 in the "sex determination" section.
Monday, January 22, 2007
Mitosis, Cell Cycle and Cancer test recap
Andrea's PSA for Angelman's Disease
More Mutations
Objective: Students will make an analogy using the terms: chromosome, gene, loci and allele to better understand the significance of those terms. Students will take notes of 5 different types of mutations and how they affect chromosomes, as well as find examples of disorders caused by mutations.
Honors Homework: none.
General Homework: create your PSA for a genetic disorder.
Sunday, January 21, 2007
54321: Update and Reminder
you are exempt from the 54321.
Friday, January 19, 2007
When Meiosis Goes Wrong (Friday 1/19 and Sat. 1/20)
Objective: Students will use a Jig-Saw method to present information on six nondisjunction disorders.
Homework: Choose a chromosomal disorder and create a public service flyer.
General class: in addition to discussion nondisjunction, will wrap up meiosis by creating a decorating cookies with the stages of meiosis.
Here's a slide show of decorating cookies. See how many stages of meiosis you can identify. HINT: (even though the pictures are blurry, you can see: metaphase 1, prophase 2, metaphase 2 and interphase)
Thursday, January 18, 2007
Meiosis with Pop-it Beads
Objective: Students will use pop-beads from Carolina Biological supply to gain hands-on experience in manipulating chromosomes in meiosis. Students will complete a comparison chart of meiosis and mitosis, along with several questions.
NOTE: while the objective sounds glorious, anyone who has ever done this activity realizes it can be like herding an elephant with a toothbrush....fortunately, there were no elephants...just slightly smaller mammals.
Homework: Turn in your second Navigating the Scientific Literature (a quiz grade) if you haven't already done so.






